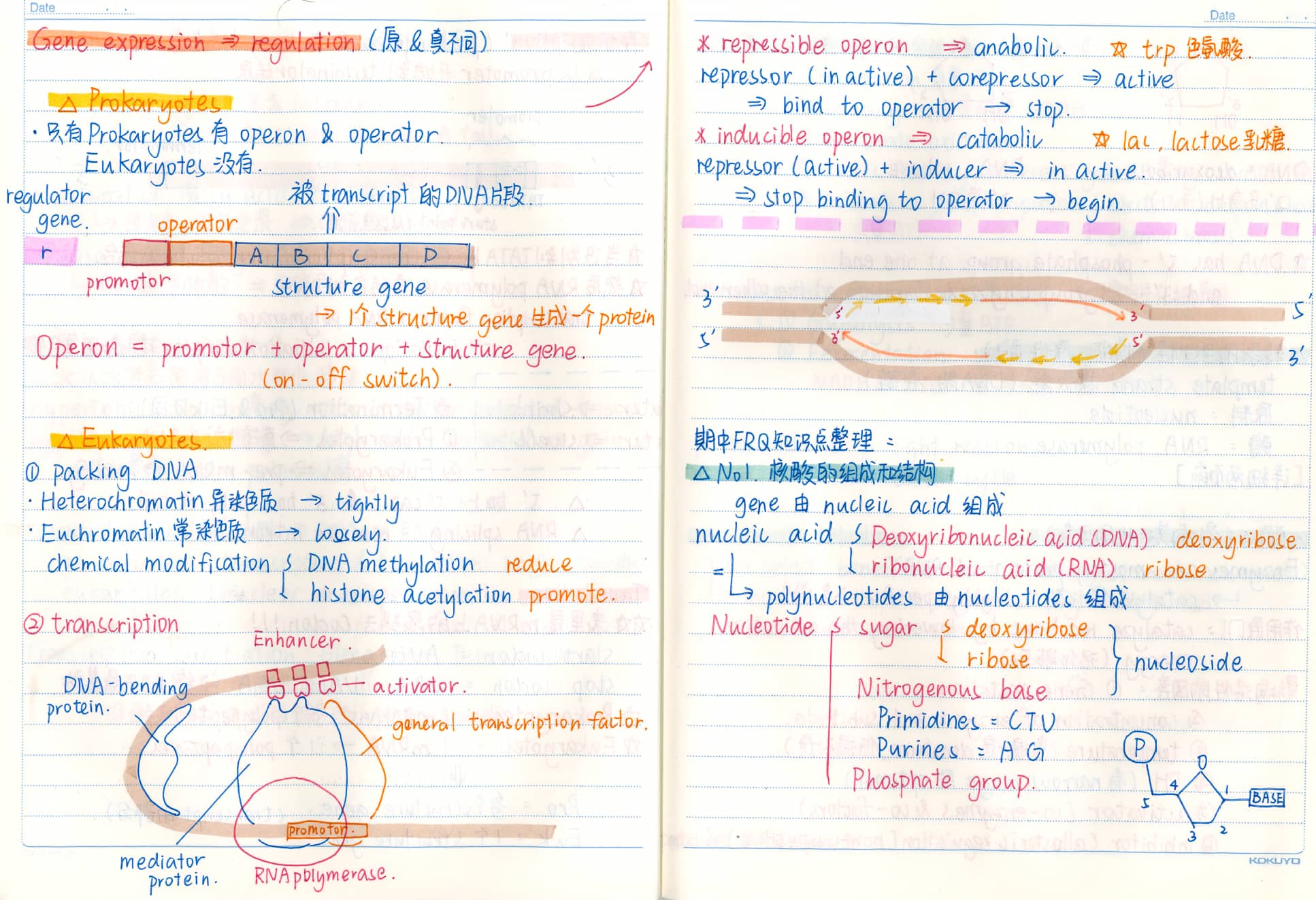
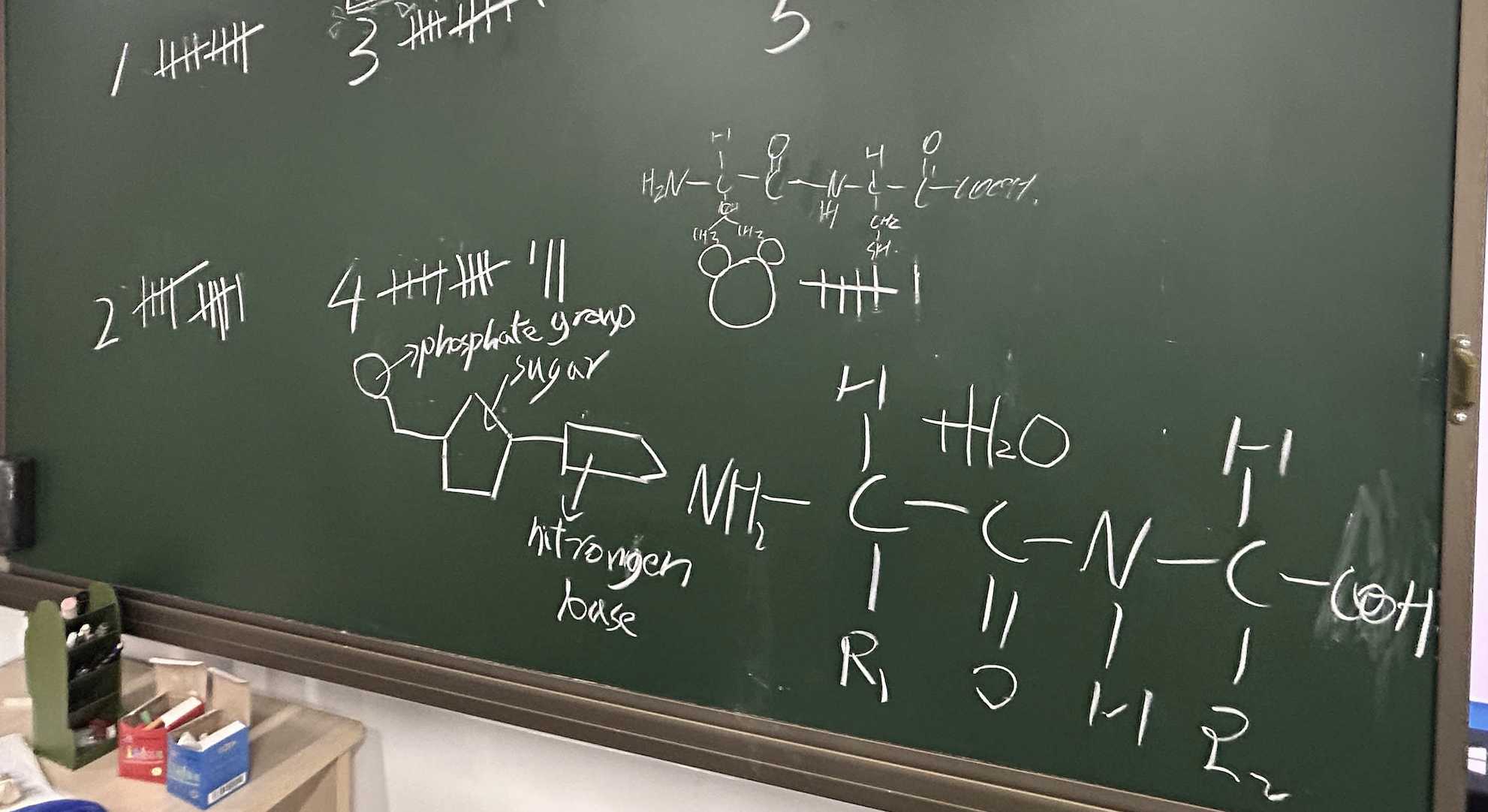AP Biology AP生物是美国大学理事会提供的高中课程,旨在帮助学生掌握大学水平的生物学知识。课程内容涵盖四大主题:进化、细胞过程(包括能量和通讯)、遗传和信息传递、以及生物系统的相互作用。AP生物学强调实验和数据分析,培养学生的科学思维能力。学生在完成课程后可以参加AP考试,如果成绩优异,可以在大学获得学分或高级课程资格。 AP Biology (Advanced Placement Biology) is a high school course offered by the College Board in the United States, designed to help students master college-level biology knowledge. The course covers four main themes - Evolution, Cellular processes (including energy and communication), Genetics and Information transfer, and interactions of biological systems. AP Biology emphasizes experiments and data analysis, fostering students’ scientific thinking skills. Upon completing the course, students can take the AP exam, and high scores may earn them college credit or advanced placement.
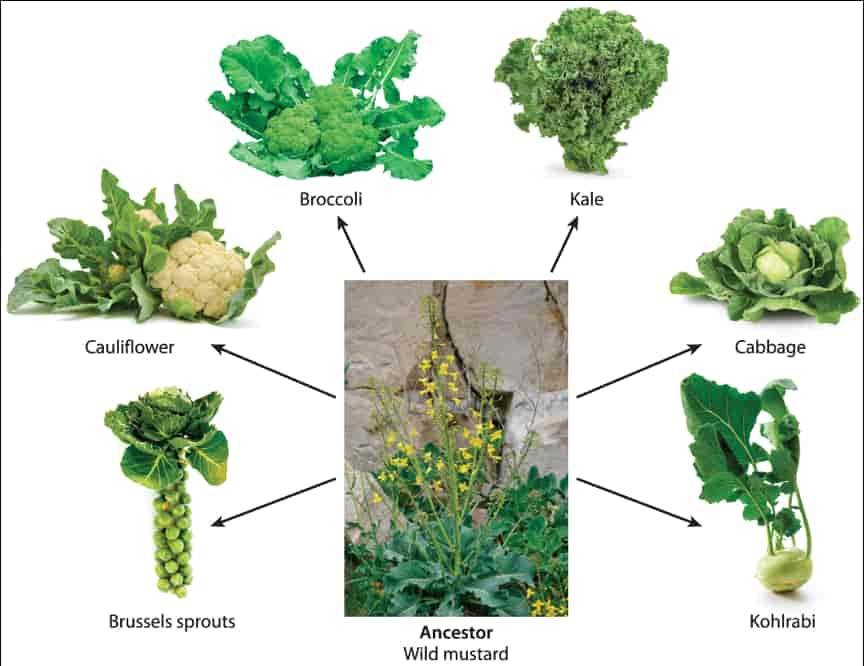
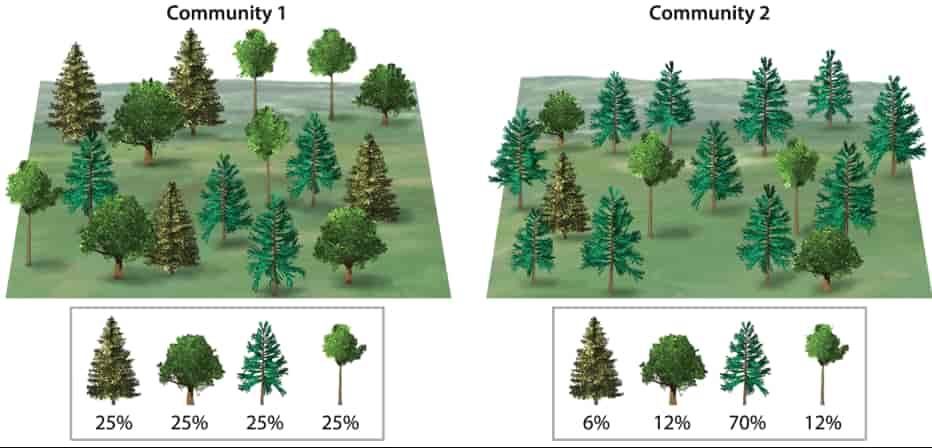
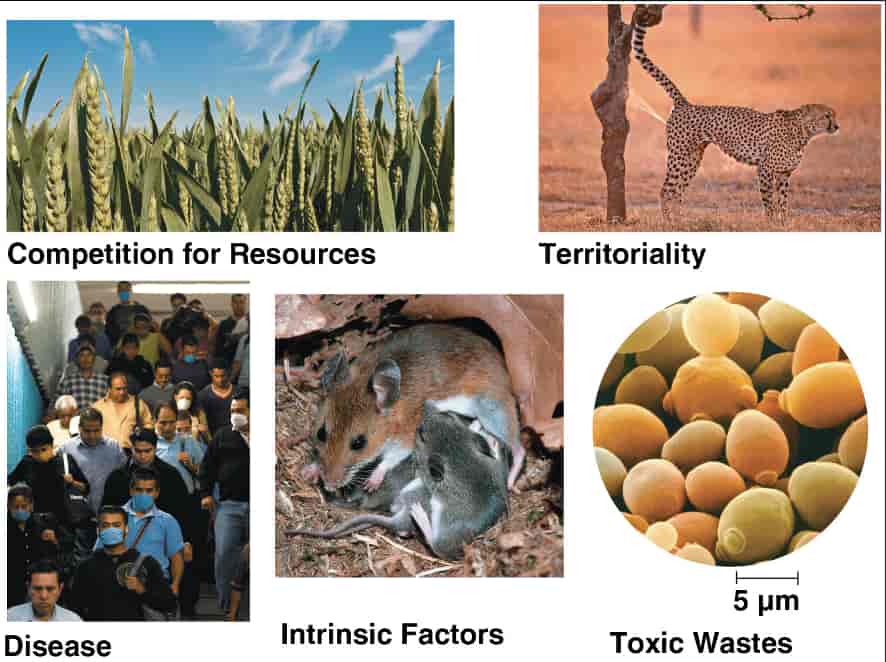
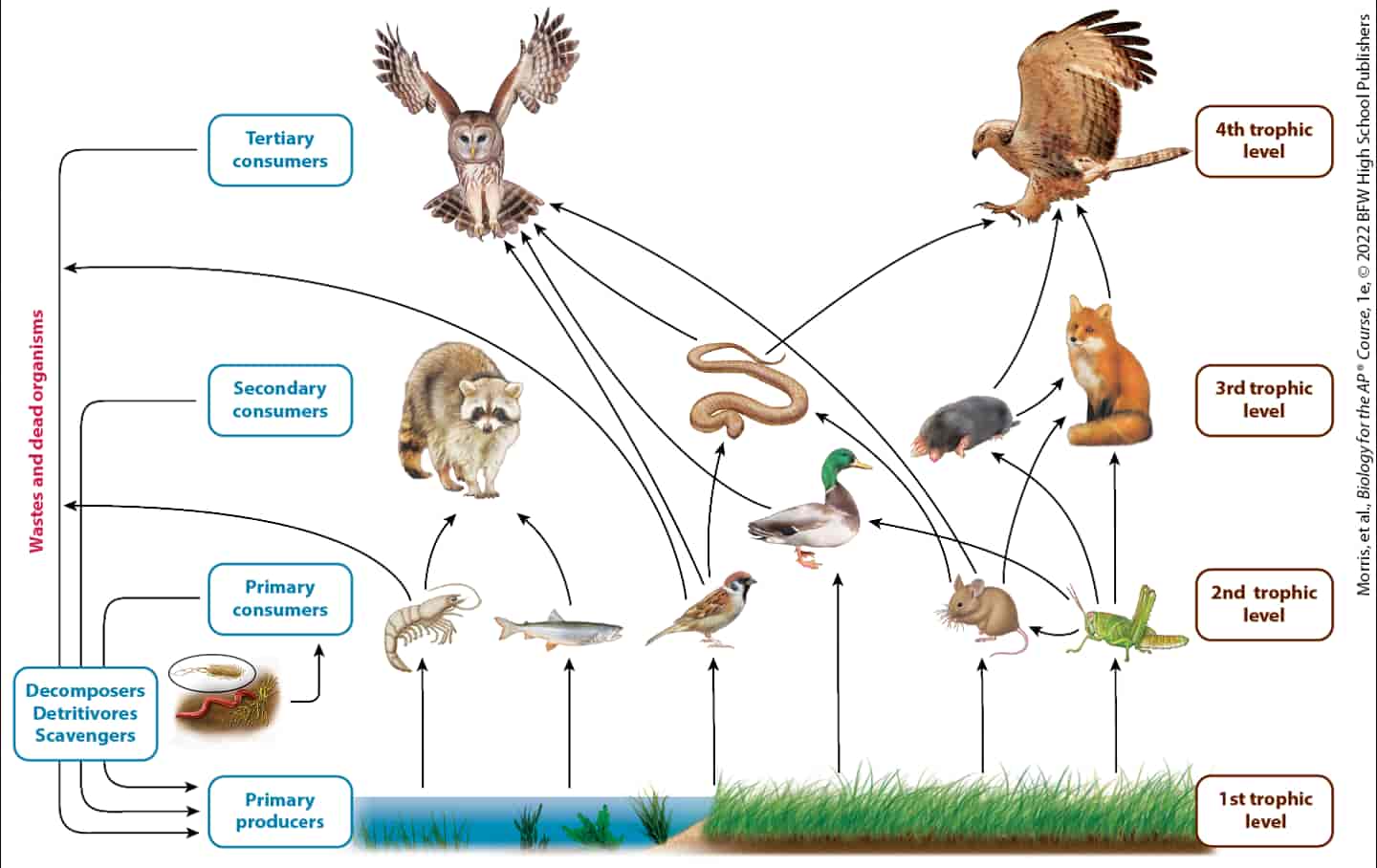
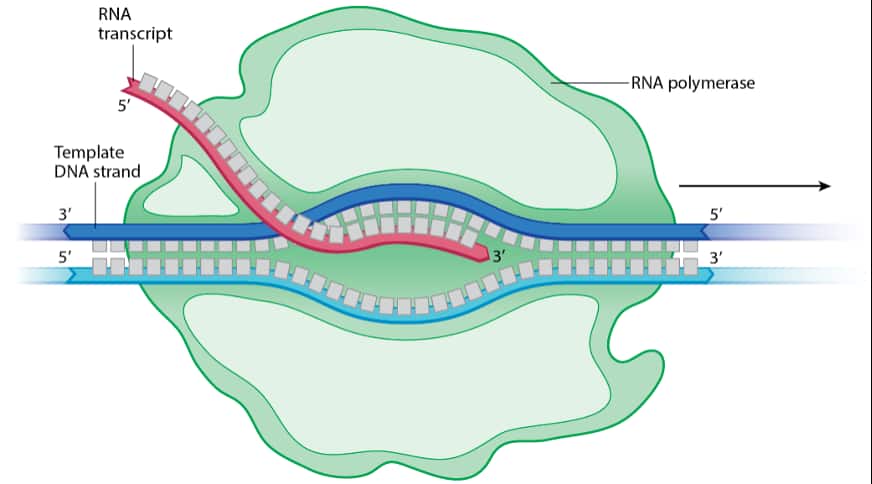
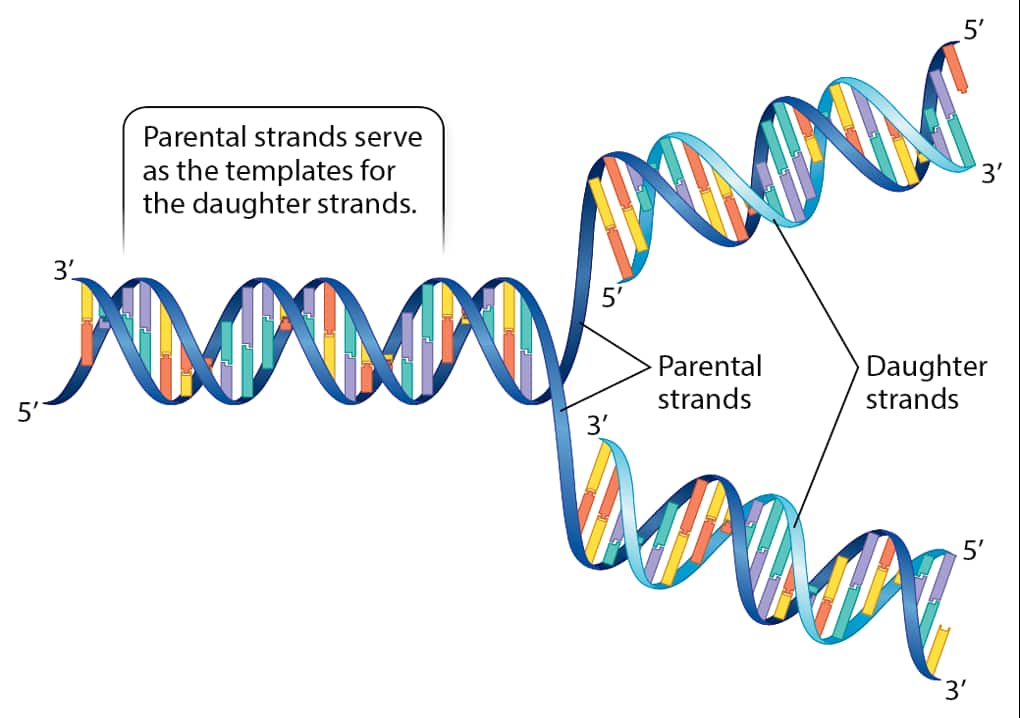
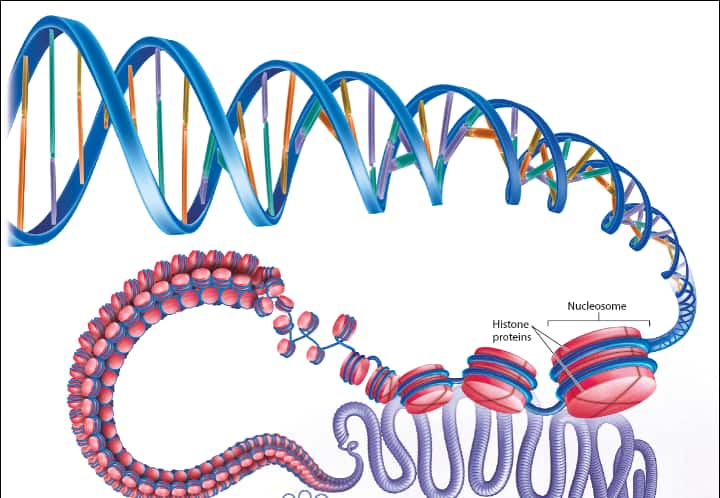
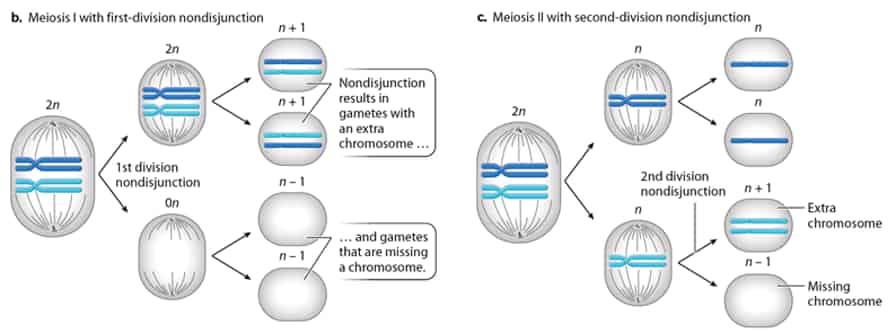
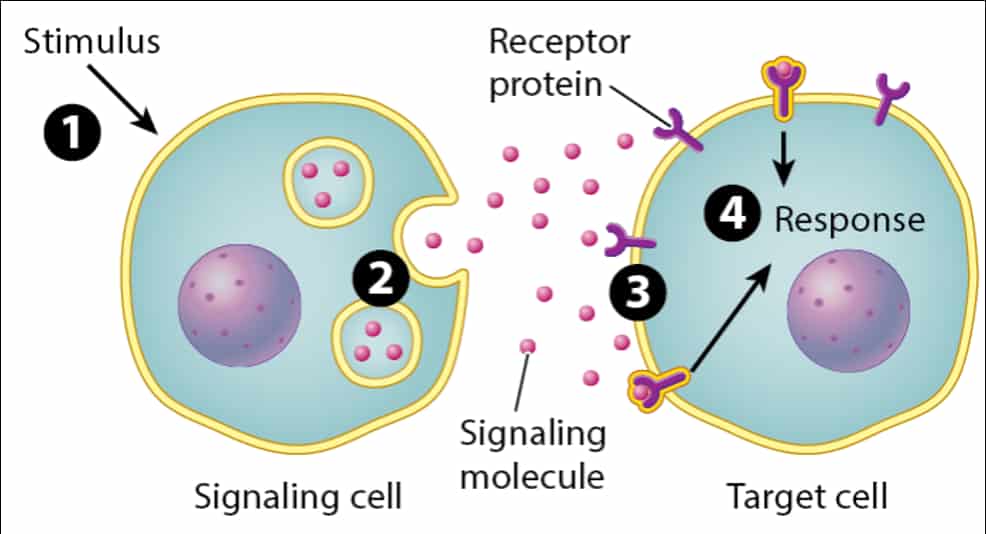
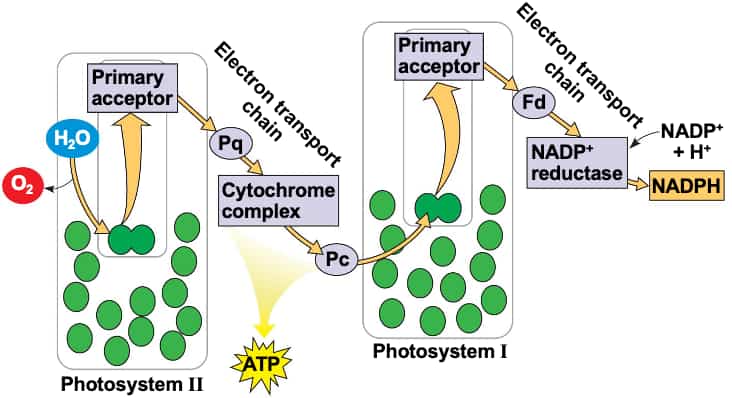
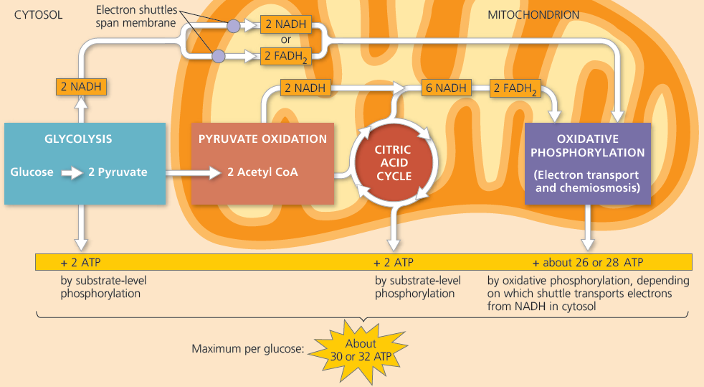
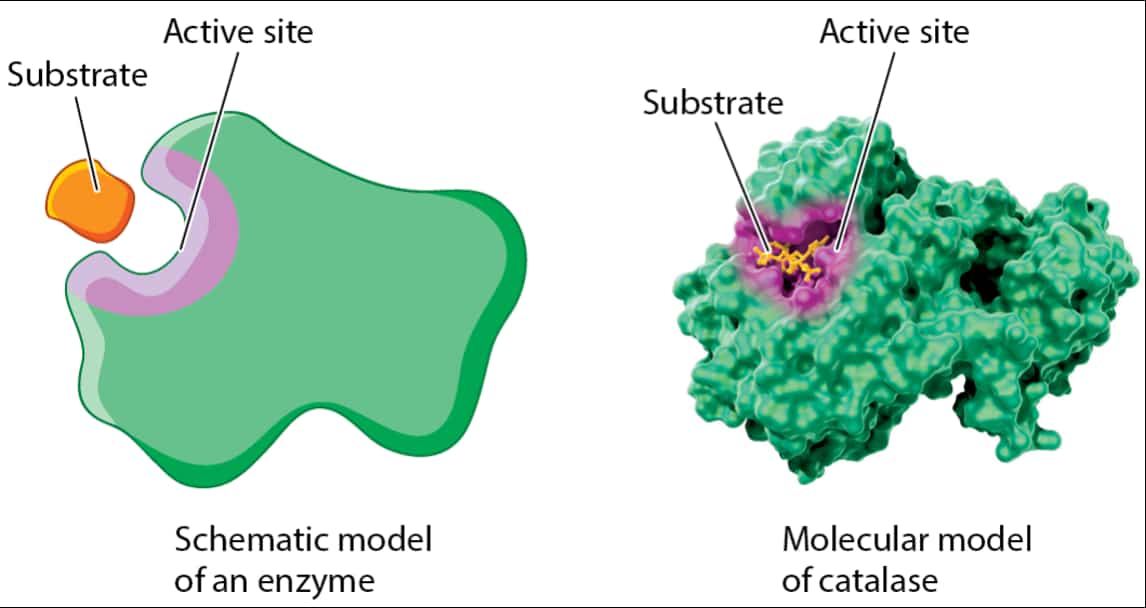
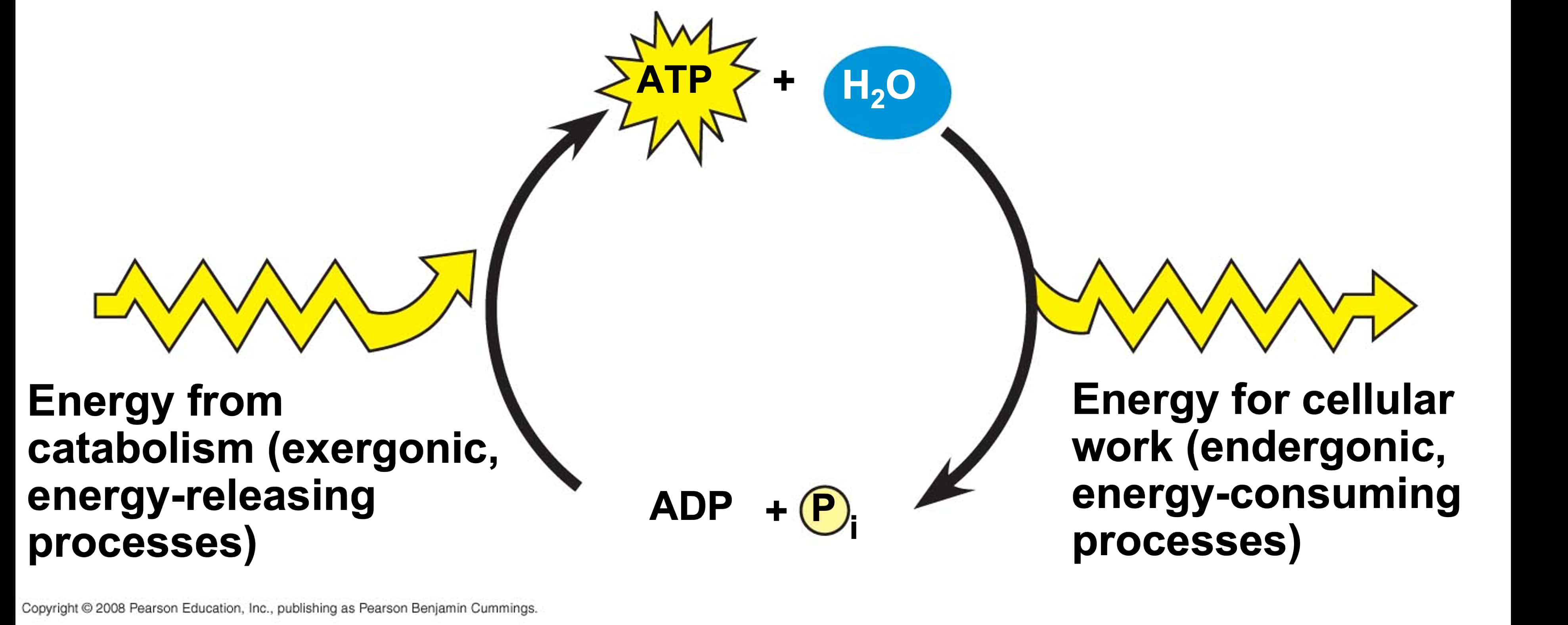
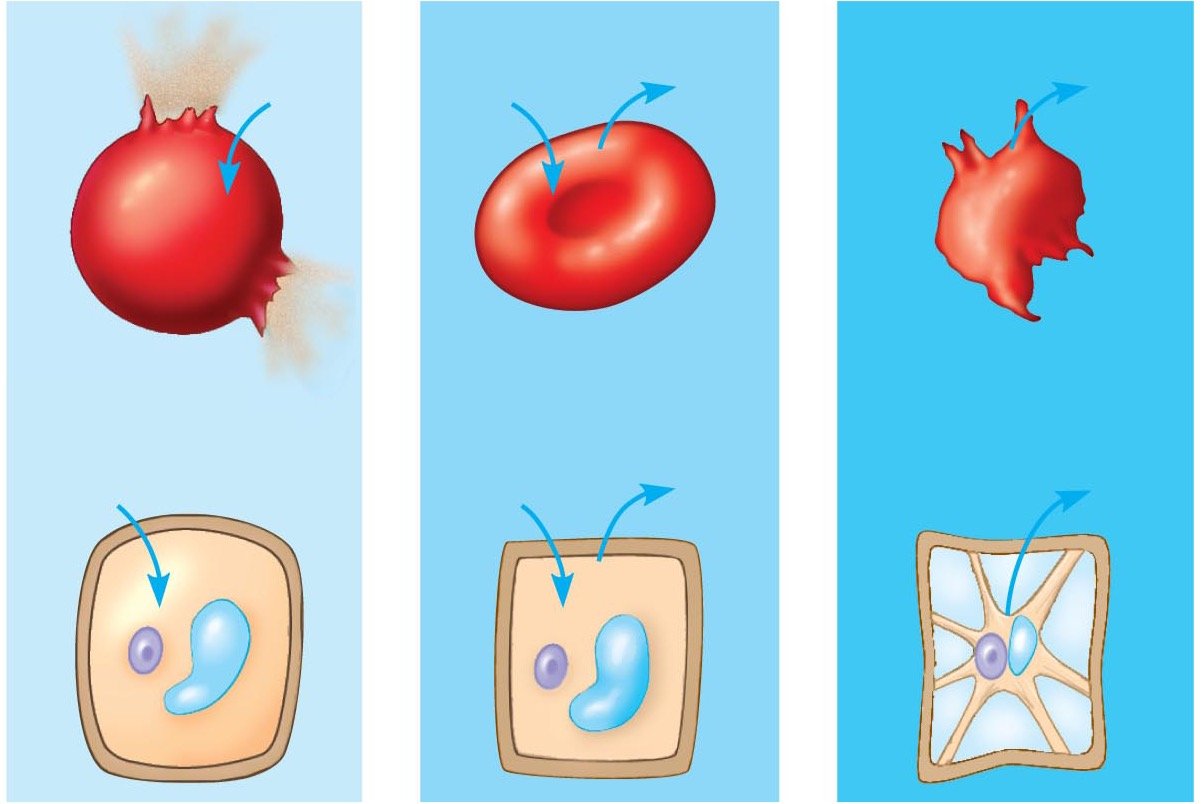
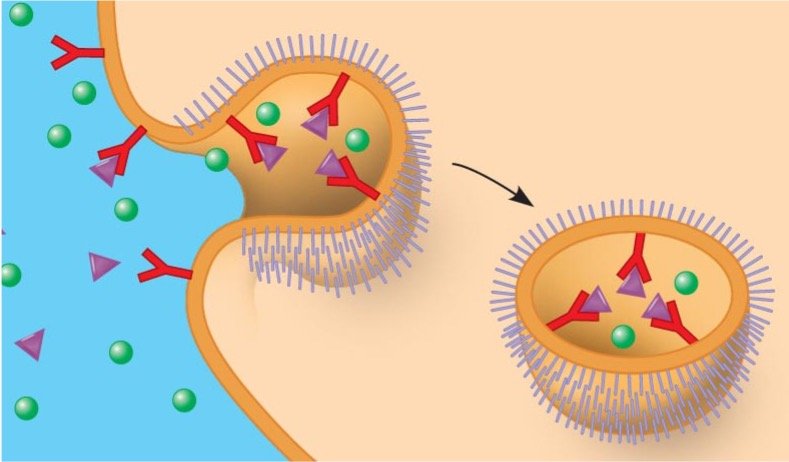
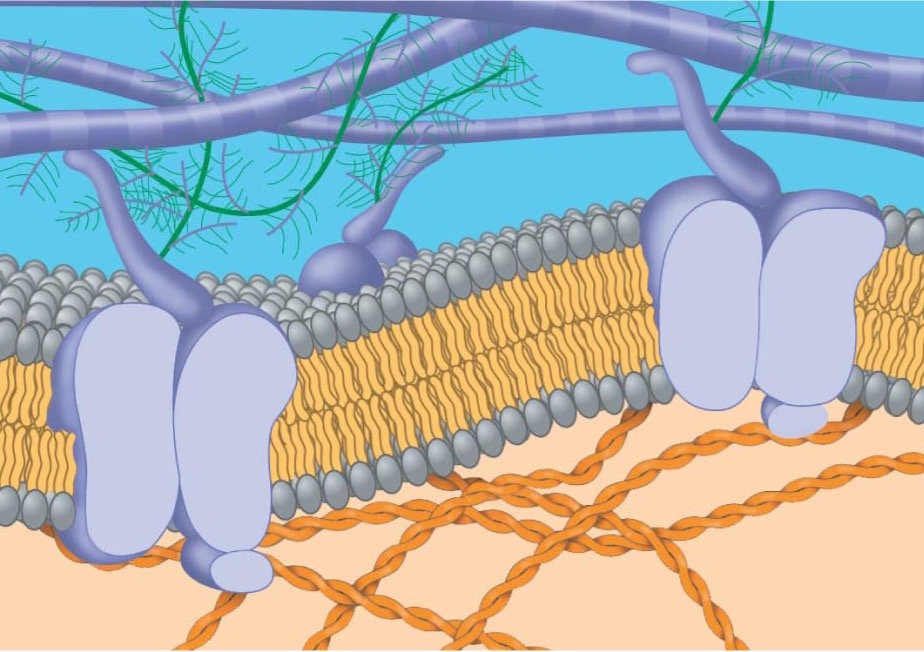
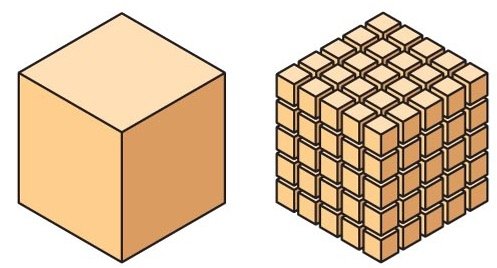
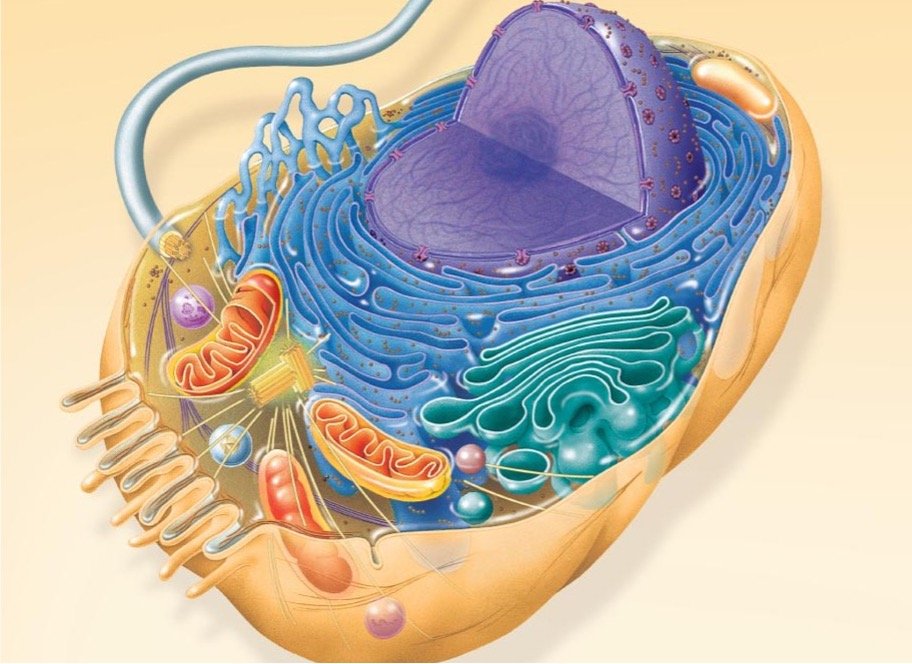
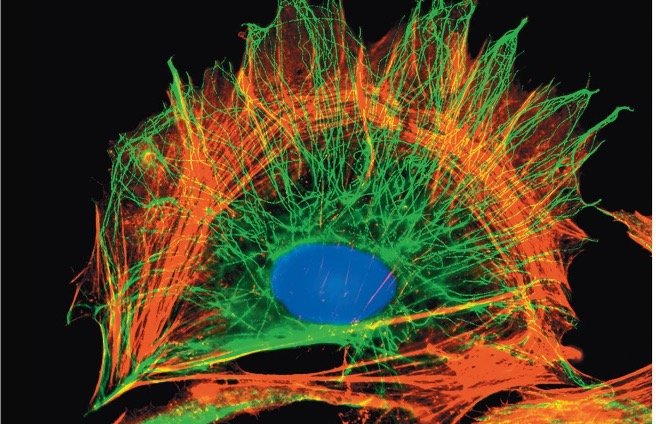
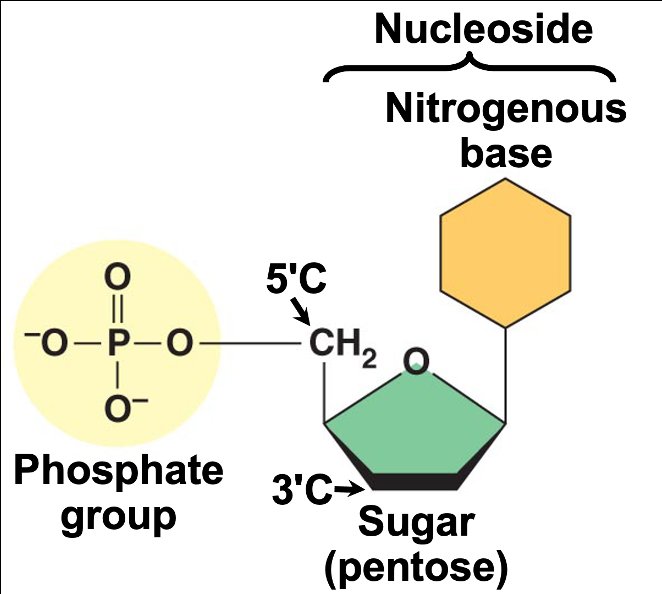
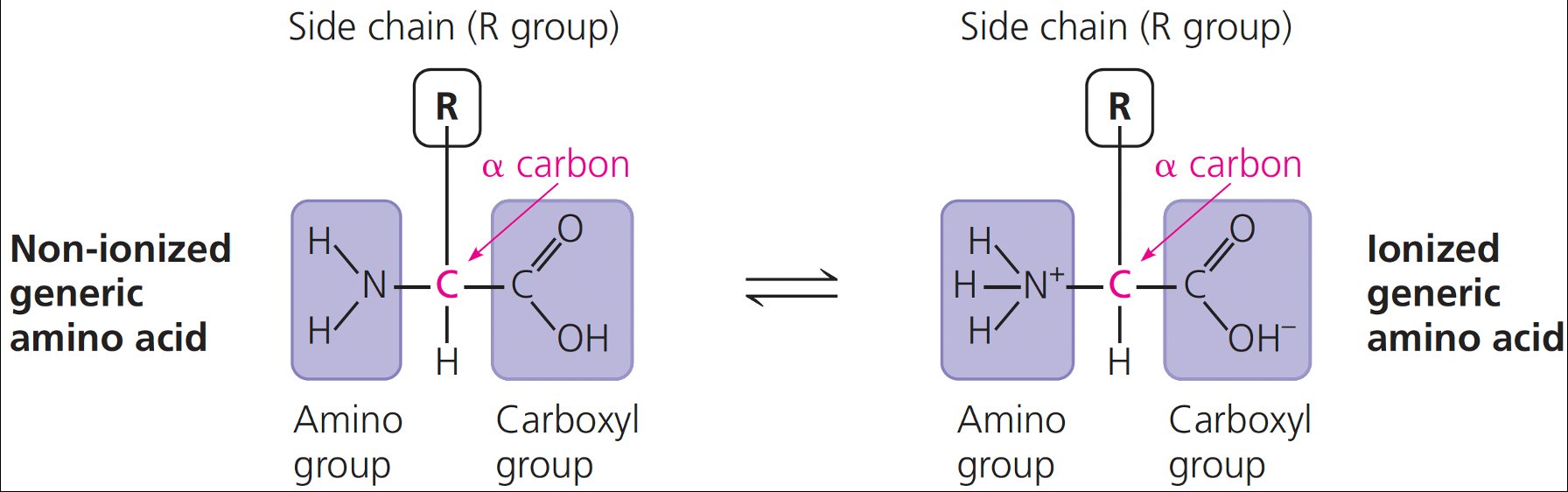
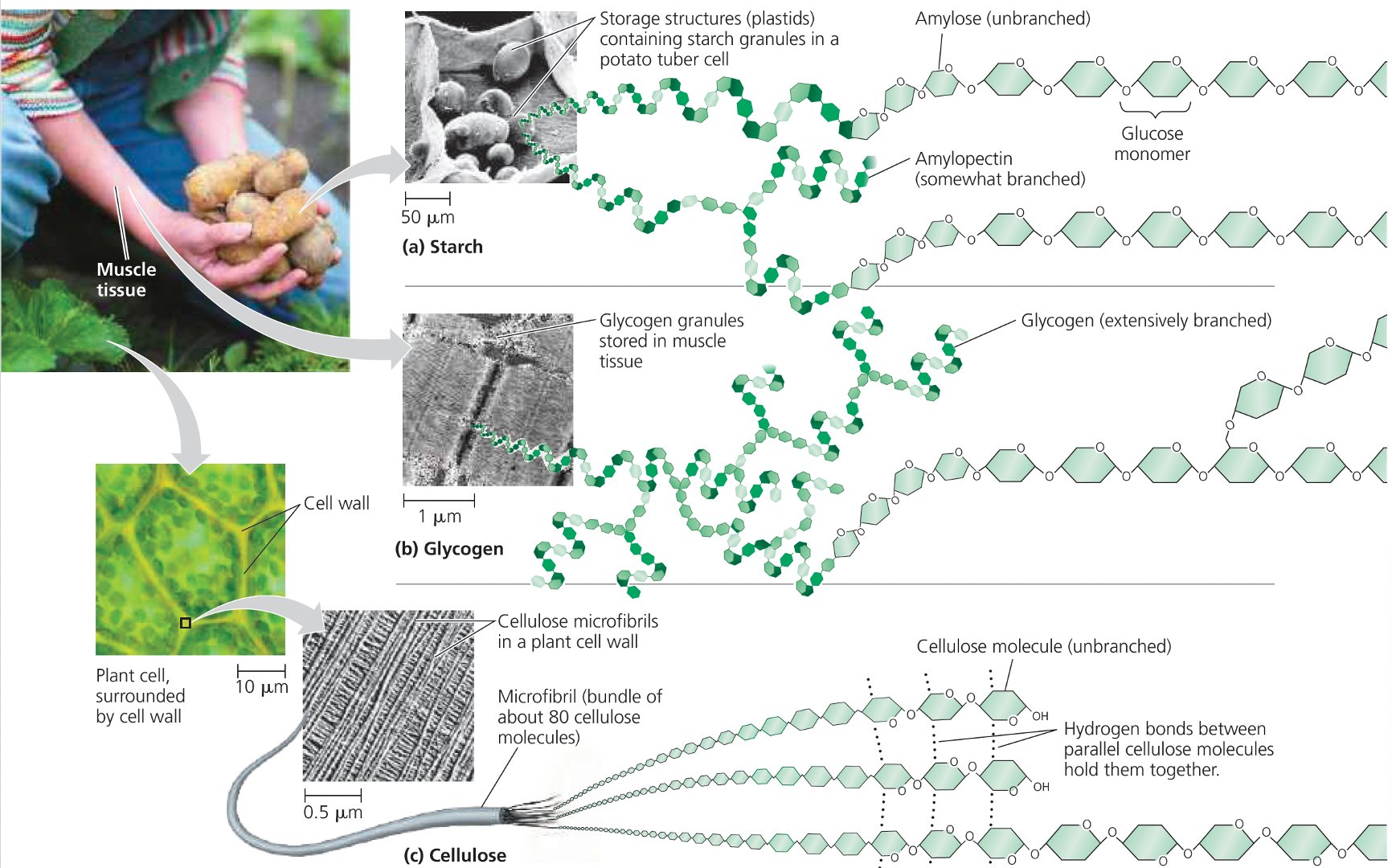
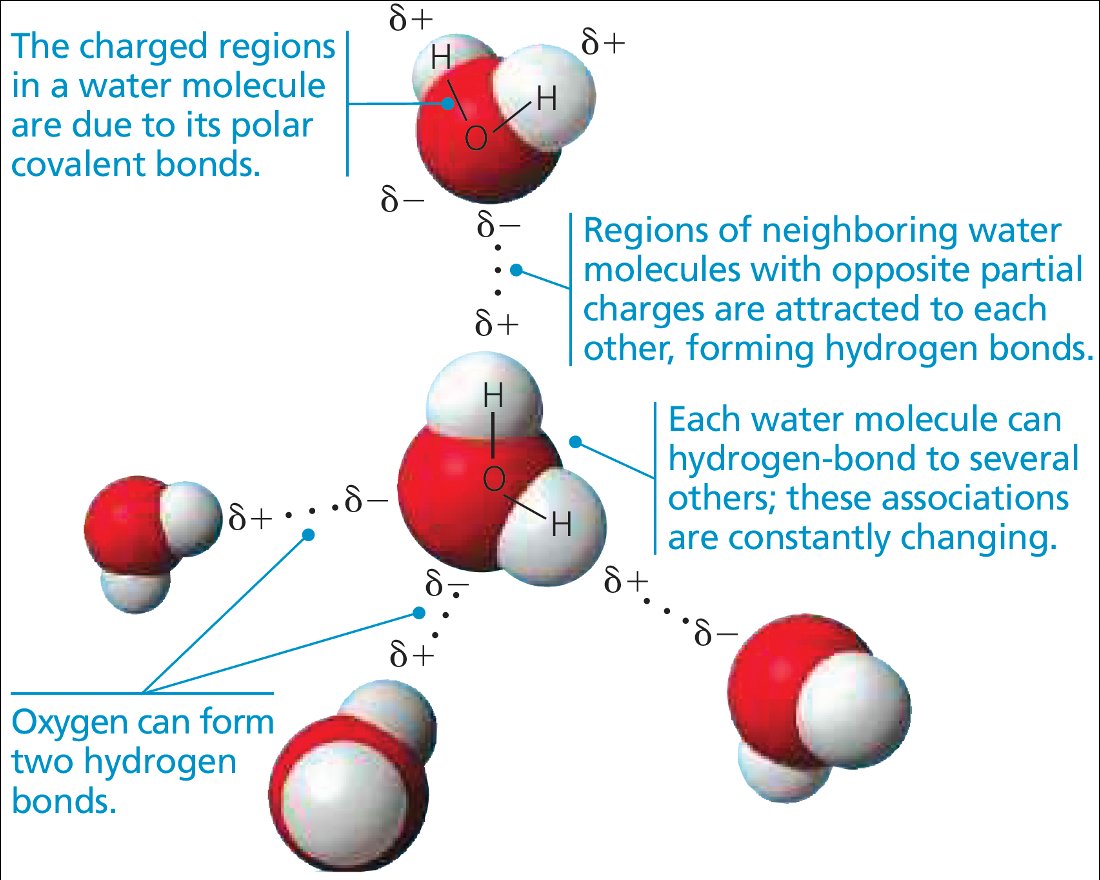
自七月七日AP出分已经过去一个月了,在阅读过Biobloom上其他同学的感受后,我也想向没有学过AP生物的同学介绍一下这个学科。 付出多少,得到多少。知道这一点时,不论结果如何,至少不会后悔什么。 A Journey of Notes, Biology, and a 5 AP生物,一个常年5分率不到两位数的学科,在今年的五分率反常的达到了19%,这究竟是一个什么预兆,现在我们不得而知。 终于可以写AP生物的总结了。5.5考完心惊胆战了两个月,一直在算分,最后真是长舒一口气:) Get inspired by AP Biology students who nailed exam prep! Master AP Bio Multiple Choice Questions with Ease! “AP生物迷思”特别汇总了一系列来自于网络的教学视频,专注于大家最困惑的知识点。 The long-term objective of restoration is to return an ecosystem as much as possible to... Biodiversity can be considered at three main levels: Genetic diversity, Species diversity, Ecosystem diversity. A biological community is an assemblage of populations of various species living close enough for... A birth rate or death rate that does not change with population density is density... Population ecology is the study of factors affecting the size of a population and how... Ecosystem dynamics involve two main processes: energy flow and chemical cycling.Energy enters most ecosystems as... Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and the environment. These interactions... Two major hypothesis for life on Earth. Panspermia: Life from extraterrestrial life. Abiogenesis: Life from... Variants that are well adapted to one environment may not be well adapted to another... Extinction is the loss of a group of organisms, such as a species. Levels of... Speciation, the origin of new species, is at the focal point of Darwin’s evolutionary theory.... Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species. The discipline... Evolution has led to new, rapidly spreading diseases, called emerging diseases. Biogeography provides information about the evolutionary history of organisms, specifically where they originated and how... When certain conditions are met, allele and genotype frequencies do not change, a state called... Natural selection acts on individuals, but only populations evolve. Genetic variations in populations contribute to... Natural selection is the differential reproductive success of genetic variants and was independently conceived by... “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution”—Theodosius Dobzhansky. A virus consists only of nucleic acid, proteins, and sometimes a membranous envelope. After infecting... Alterations in a DNA sequence can lead to changes in the type or amount of... Embryonic cells become committed to a certain fate (determination), and undergo differentiation, becoming specialized in... All organisms, whether prokaryotes or eukaryotes, must regulate which genes are expressed at any given... Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide using the information in the mRNA. During this... Transcription is the synthesis (production) of RNA using information in the DNA. The two nucleic... Watson and Crick’s model predicts that when a double helix replicates, each of the two... The elegant double-helical structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) shook the scientific world when it was... Chromosomal inheritance can result in mutations that increase genetic diversity but can also cause genetic... Another departure from simple Mendelian genetics arises when the phenotype for a character depends on... In the 1900s, geneticists extended Mendelian principles not only to diverse organisms, but also to... Modern genetics began during the mid-1800s with a monk named Gregor Mendel, who discovered the... Gamete formation involves a type of cell division called meiosis. This type of cell division... Levels of proteins called cyclins increase and decrease during the cell cycle. Cyclins were discovered... Mitosis is just one part of the cell cycle, the life of a cell from... Negative feedback helps to maintain homeostasis. Positive feedback is self-reinforcing and amplifies responses. Food and drugs can be sources of chemicals that act as exogenous ligands in cell... Signal Transduction pathways differ in specific details, but have certain, unifying characteristics. All pathways follow... Cells communicate by sending and receiving chemical messengers. Cells can communicate over various distances Dive into the essential concepts of biostatistics to bolster your exam preparation and scientific inquiry... The conversion process that transforms the energy of sunlight into chemical energy stored in sugars... Respiration breaks the fuel down, using oxygen and generating ATP. The waste products of this... Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers. Each enzyme has an optimal temperature... The totality of an organism’s chemical reactions is called metabolism. Metabolism is an emergent property... Membranes and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells compartmentalize intracellular metabolic processes and specific enzymatic reactions.... The diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane, whether artificial or cellular, is... Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy investment. Active... In fluid mosaic model, the membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a... The surface-to-volume ratio is an important parameter affecting cell size and shape. Cells—the basic structural and functional units of every organism—are of two distinct types: prokaryotic and... The cell is an organism’s basic unit of structure and function. Many forms of life... Nucleic acids are polymers made of monomers called nucleotides. Nucleic acids store, transmit, and help... Proteins are all constructed from the same set of 20 amino acids, linked in unbranched... Carbohydrates include sugars and polymers of sugars. The simplest carbohydrates are the monosaccharides, or simple... Water (H2O) is made up of two hydrogen atoms covalently bound to an oxygen atom.... Matter is made up of elements. An element is a substance that cannot be broken... © 2024. All rights reserved.
总访问量