Central Dogma - Flash Talk
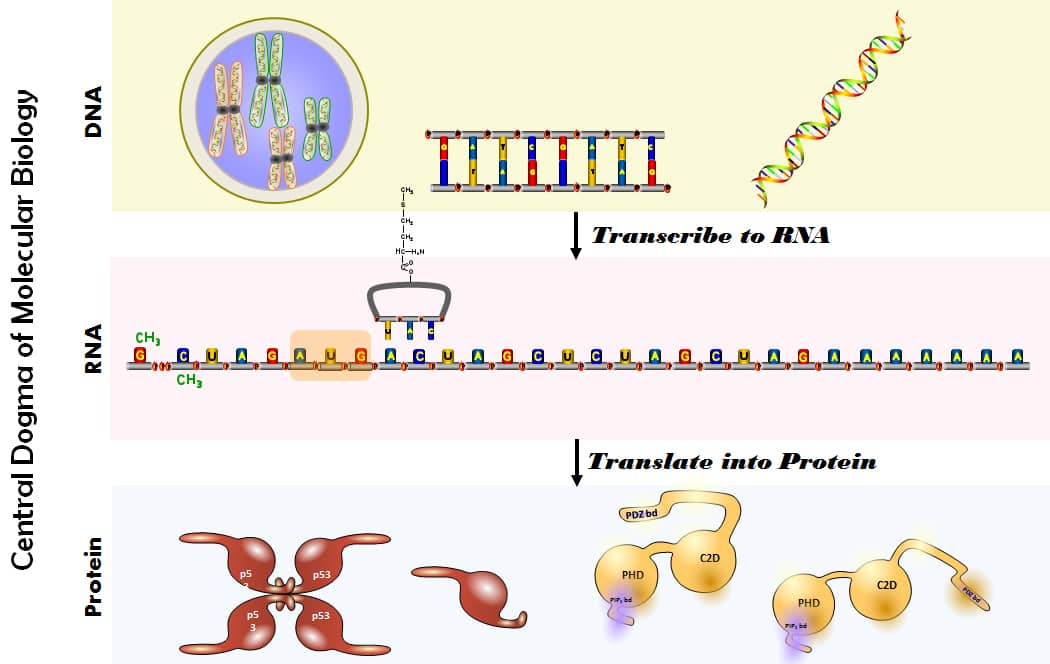
A flash talk is a brief speech or presentation, intended to grab the attention of the audience and convey key information in a quick, insight, and clear manner.
Flash Talk: Protein Synthesis

A flash talk is a brief speech or presentation, intended to grab the attention of the audience and convey key information in a quick, insight, and clear manner.
Flash Talk: Protein Synthesis

愿新的一年里,大家健康快乐、学业有成,勇敢追逐自己的梦想!
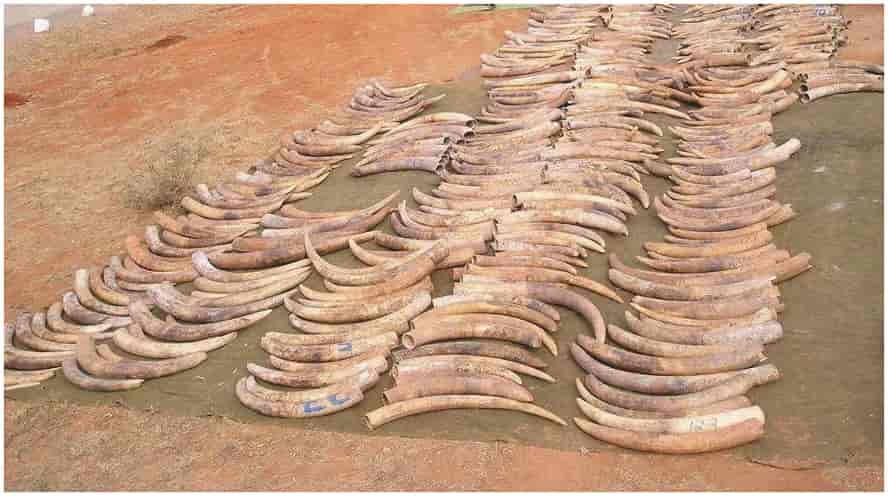

The long-term objective of restoration is to return an ecosystem as much as possible to its predisturbance state. Two key strategies are employed in restoration: bioremediation and biological augmentation.
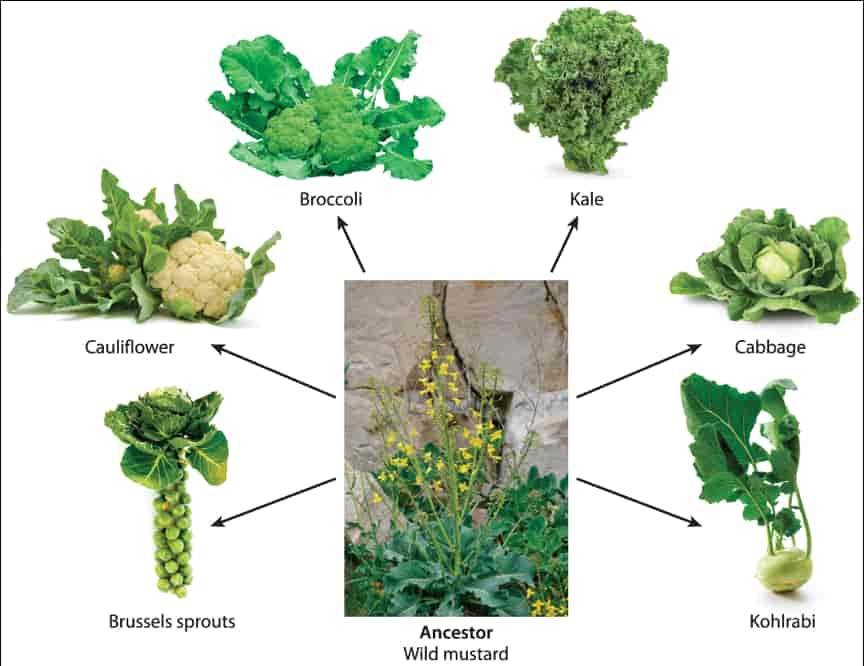
Biodiversity can be considered at three main levels: Genetic diversity, Species diversity, Ecosystem diversity.
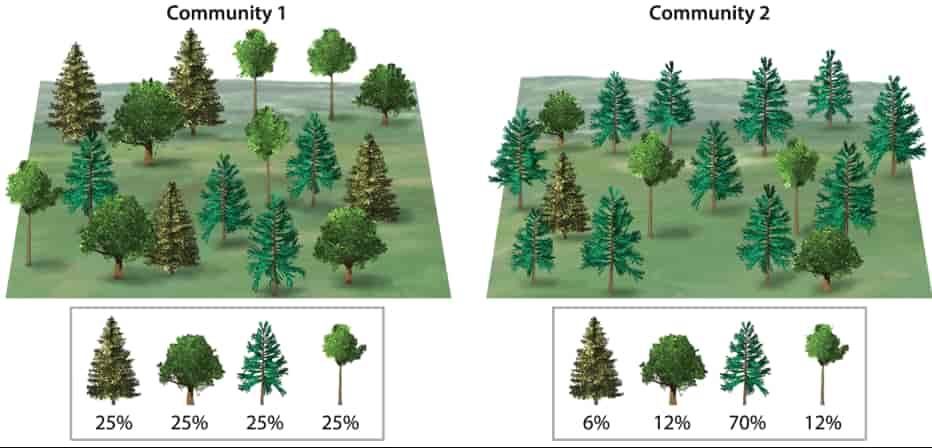
A biological community is an assemblage of populations of various species living close enough for potential interaction.
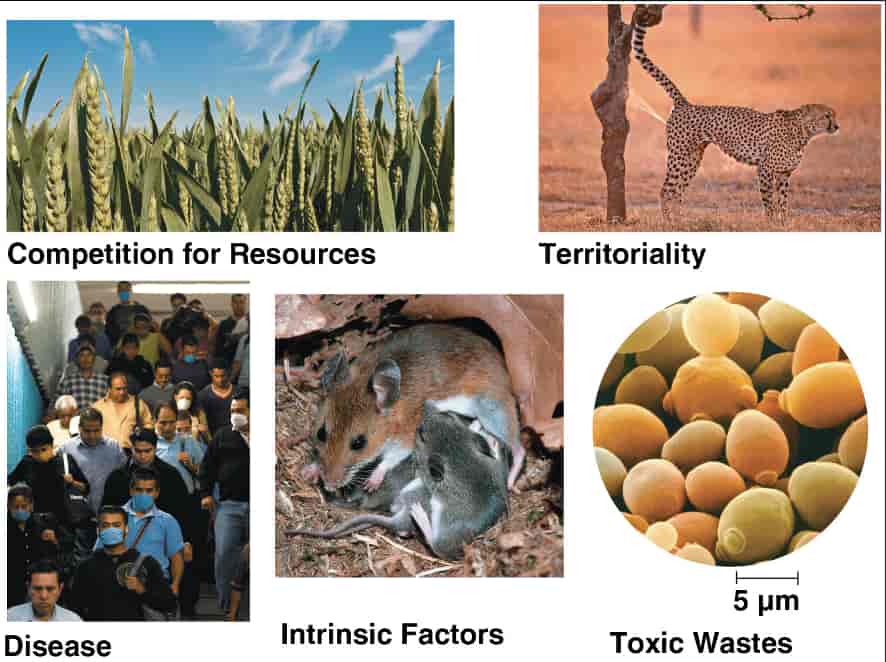
A birth rate or death rate that does not change with population density is density independent. If a death rate increases or a birth rate decreases with increasing density, it is density dependent.
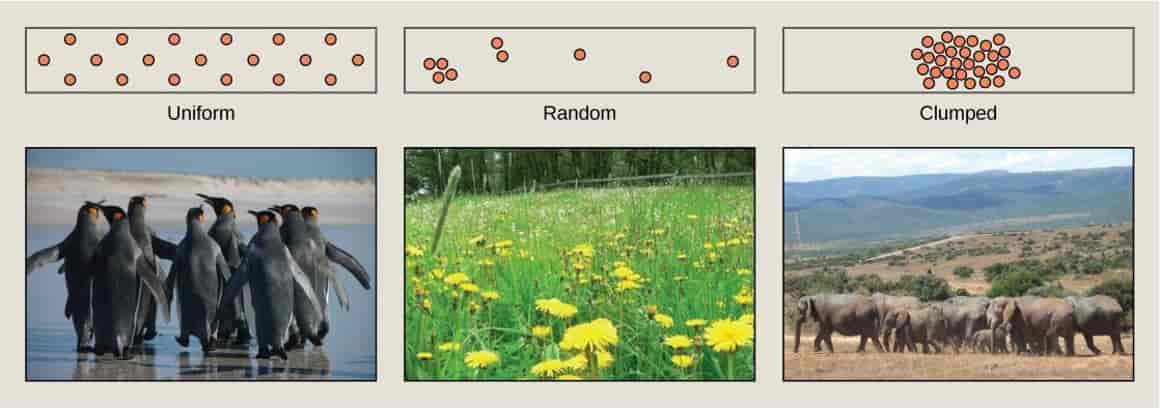

Population ecology is the study of factors affecting the size of a population and how it changes over time.
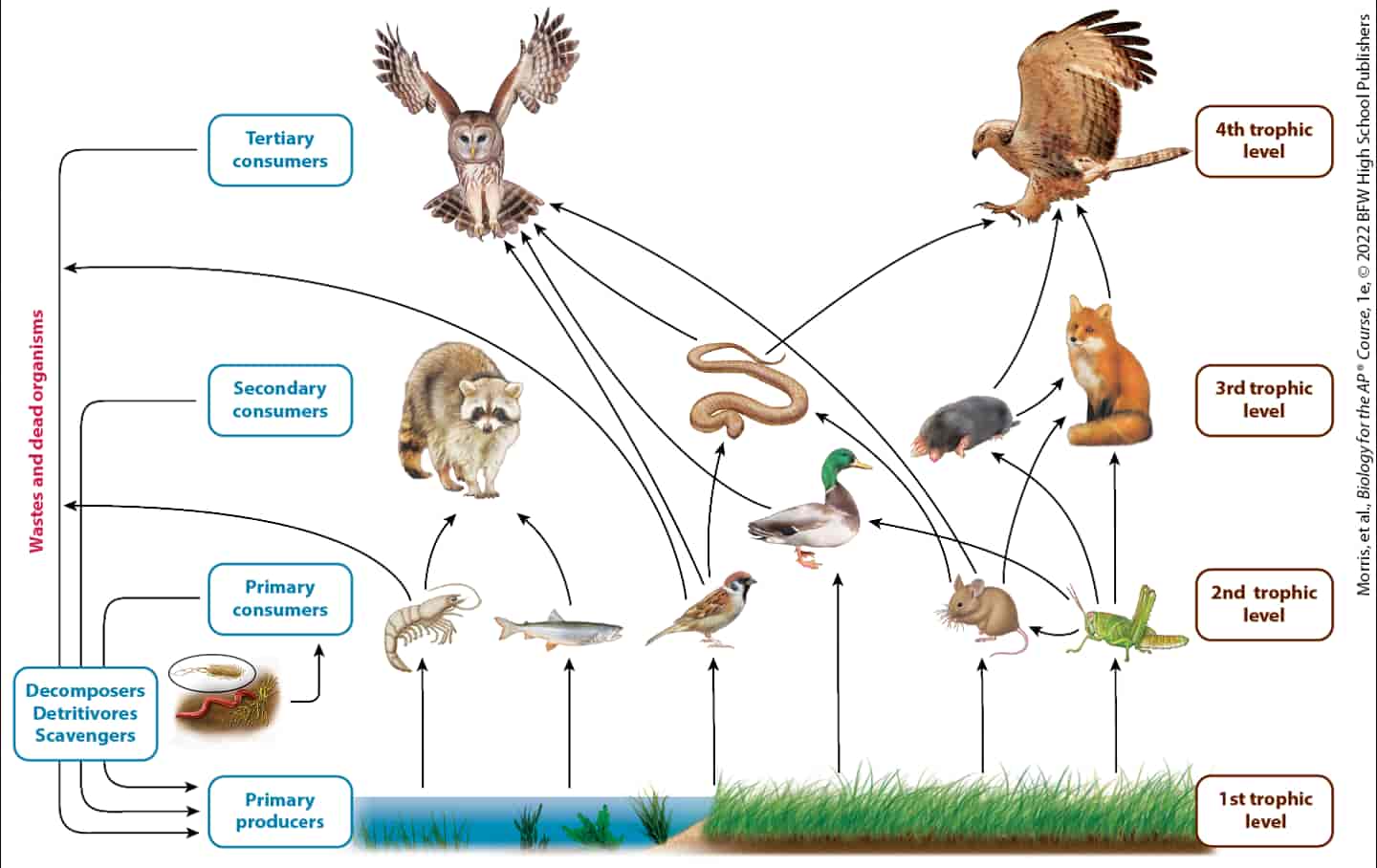
Ecosystem dynamics involve two main processes: energy flow and chemical cycling.Energy enters most ecosystems as sunlight, is converted to chemical energy by autotrophs, passed to heterotrophs as food, and dissipated as heat.
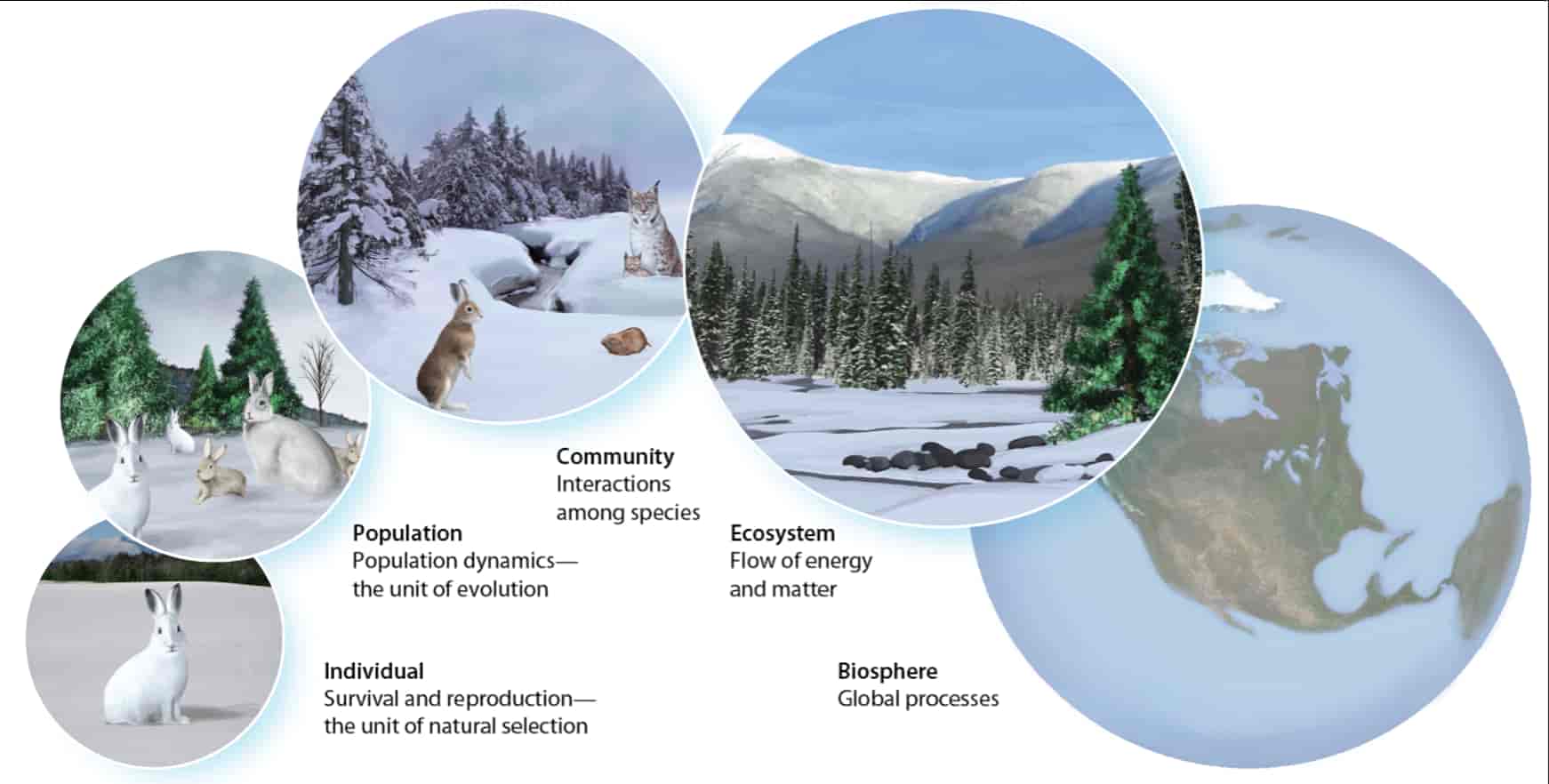
Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and the environment. These interactions determine both the distribution of organisms and their abundance.
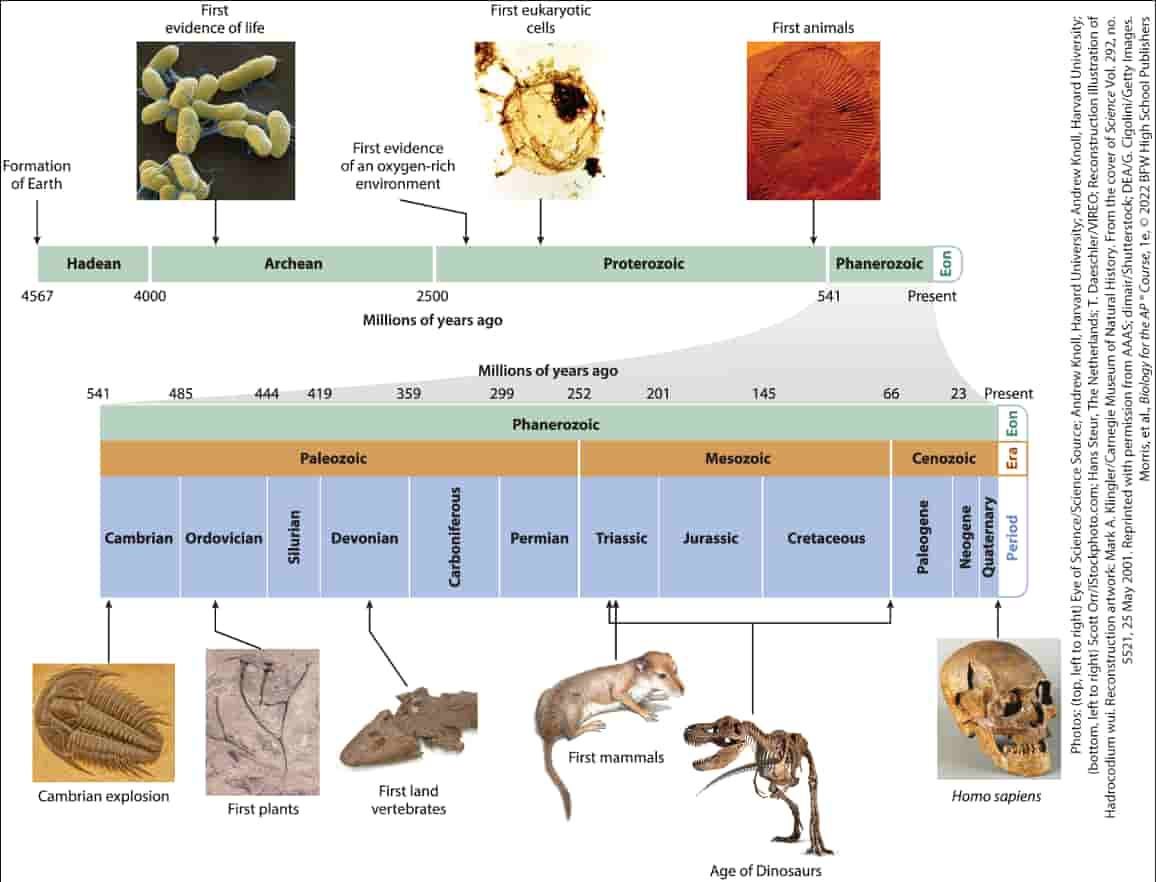
Two major hypothesis for life on Earth. Panspermia: Life from extraterrestrial life. Abiogenesis: Life from non-life. Requires 4 major milestones to occur.